HVAC systems rely on motor technology for optimal performance, energy efficiency, and operational cost. PSC motors are simple, durable, and cost-effective, ideal for applications that don't require variable speed control. ECMs are brushless DC motors that use a built-in inverter and microcontroller, adjust their speed to the heating or cooling demand, and can be up to 30% more efficient than PSC motors. The choice between PSC motors and ECMs depends on the specific needs of the HVAC system.
Understanding PSC Motors
Permanent Split Capacitor (PSC) motors have been the backbone of the HVAC industry for decades. They are simple, durable, and cost-effective, making them suitable for various applications. The working principle of a PSC motor is based on electrical capacitance and induction. It consists of a run capacitor permanently connected in series with the start winding. This setup creates a phase shift in the motor's magnetic field, which induces rotation. Due to their simplicity, PSC motors are ideal for applications that do not require variable speed control.
How PSC Motors Work
PSC motors operate on a relatively straightforward mechanism, incorporating a run capacitor permanently wired to the start winding. This facilitates a phase shift in the motor's magnetic field to induce rotation. This design features two principal windings: the start and the main winding. When the motor is powered, the interaction between the capacitor and the windings creates a lag in the electrical current, generating a magnetic field that propels the rotor to turn. The operational essence of PSC motors is their reliance on a fixed speed, which is predominantly determined by the power supply frequency and the specific construction of the motor itself. This simplicity in design and function makes PSC motors a popular choice for applications where variable speed is unnecessary, offering a reliable and uncomplicated solution.
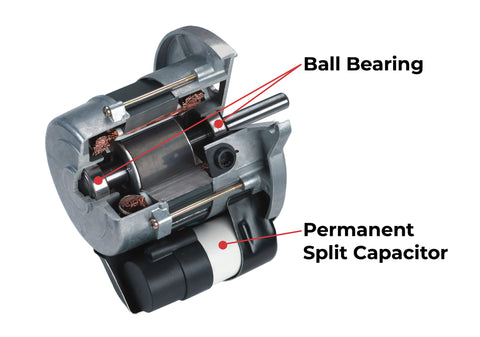
Advantages of PSC Motors
- Cost-effectiveness – Their simple design makes PSC motors relatively inexpensive to produce and purchase.
- Reliability – With fewer moving parts and electronic components, PSC motors are known for their durability and long service life.
Limitations of PSC Motors
- Efficiency – PSC motors are less efficient, especially at partial load conditions, leading to higher energy consumption.
- Speed Variability – They offer limited flexibility in speed control, which can be a disadvantage in applications requiring variable airflow.
Exploring ECM Technology
Electronically Commutated Motors (ECM) represent a significant advancement in motor technology. They combine the efficiency of DC motors with the practicality of AC power. ECMs are brushless DC motors that use a built-in inverter and microcontroller to control motor speed and torque efficiently. This smart technology allows ECMs to adjust their speed to the heating or cooling demand, significantly reducing energy consumption.
How ECMs Work
ECMs integrate advanced technology to provide a more efficient and versatile operation than traditional motors. At their core, ECMs are brushless DC motors with a permanent magnet rotor and sophisticated electronic controls, including a built-in inverter and a microcontroller. These components work in unison to adjust the motor's speed and torque in response to varying demands. The controller dynamically alters the current within the motor's windings, allowing for a broad range of speeds and significantly enhancing the system's efficiency and adaptability. This capability to finely tune motor operation conserves energy and contributes to consistent airflow, reduced temperature fluctuations, and quieter system performance. The inherent sophistication of ECM technology marks a leap forward in HVAC motor design, offering tangible benefits in terms of energy savings and comfort.
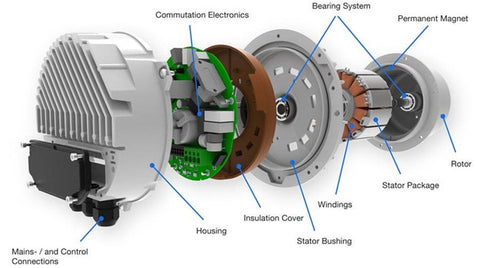
Read more about ECMs in our Understanding ECM and Variable Speed Motors in HVAC Systems blog post.
Advantages of ECMs
- Energy Efficiency – ECMs can be up to 30% more efficient than PSC motors, especially at reduced speeds.
- Variable Speed – Adjusting motor speed enhances comfort by delivering consistent airflow and reducing temperature fluctuations.
- Quiet Operation – ECMs tend to operate more quietly than PSC motors, improving the overall environment within the conditioned space.
Limitations of ECMs
- Cost – The initial investment in ECM technology is higher than for PSC motors due to the complexity and electronic components.
- Repairability – ECMs can be more challenging to diagnose and repair, requiring specialized knowledge and tools.
ECMs vs. PSC Motors
Choosing between ECM technology and PSC motors depends on the specific needs of the HVAC system, including efficiency requirements, control flexibility, and budget considerations. While PSC motors offer simplicity and cost-effectiveness for straightforward applications, ECMs provide superior efficiency, control, and comfort, making them an increasingly popular choice in modern HVAC systems.
FAQs Regarding PSC Motors vs. ECMs
What is the main difference between ECM and PSC motors?
The main difference is their efficiency and control capabilities. ECMs are more energy-efficient and can adjust their speed based on demand, leading to better system performance and lower energy consumption. PSC motors operate at a fixed speed and are generally less efficient but more cost-effective upfront.
Why are ECMs more energy-efficient than PSC motors?
ECMs feature advanced electronics that precisely control the motor's speed and torque, allowing them to operate at variable speeds and adjust to the system's demands. This reduces energy consumption, especially in partial load conditions, unlike PSC motors that run at full power regardless of demand.
Are ECMs worth the higher initial cost compared to PSC motors?
Yes, for many applications. Although ECMs have a higher initial cost, their energy efficiency and operational savings can offset the higher upfront expense over time. They also offer improved comfort and quieter operation.
Can ECMs be used to retrofit systems designed for PSC motors?
Yes, but with some considerations. Retrofitting an ECM in a system designed for a PSC motor can improve efficiency and control. However, additional adjustments or components may be required to ensure compatibility with the existing system.
How do the lifespans of ECMs and PSC motors compare?
ECMs generally have a longer lifespan than PSC motors due to their brushless design and more efficient operation, which leads to less wear and tear. However, the lifespan of any motor will depend on factors like usage patterns, maintenance, and the specific application environment.
Are ECMs more complicated to repair or replace than PSC motors?
Yes, due to their sophisticated electronics and software, ECMs can be more complex to diagnose and repair compared to the relatively straightforward design of PSC motors. Replacement parts for ECMs can also be more expensive. However, their longer lifespan and energy savings can mitigate these factors.

