In commercial HVAC systems, selecting the correct motor for pumps, blowers, and other equipment is crucial for efficiency, longevity, and reliability. When faced with the choice between TEFC (Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled) motor and Open Drip Proof (ODP) motor, understanding the nuances of each can make a significant difference. Let's delve into the specifics of TEFC vs. ODP motors to see how they align with different HVAC needs.
Totally Enclosed Fan Cooled (TEFC) Motors
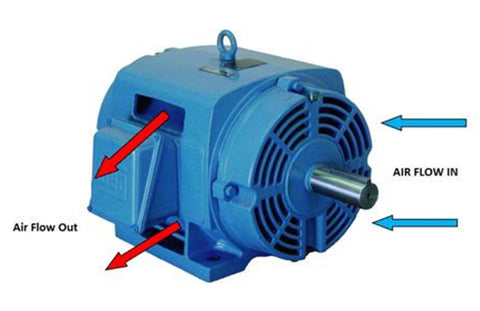
TEFC motors are designed with an outer casing that completely encloses the motor, preventing the free exchange of air between the inside and outside of the motor. This enclosure has external fins that increase the surface area for cooling. A fan attached to the shaft blows air over the motor casing, facilitating the removal of excess heat. The design of TEFC motors makes them more resilient to dust, moisture, and other environmental contaminants.
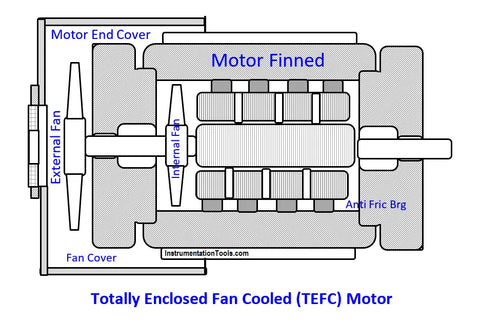
TEFC motor enclosures are highly versatile and can be used in a wide range of HVAC applications, especially in environments where motor exposure to dust, moisture, and other airborne particles is a concern. They are ideal for driving equipment such as pumps and blowers in outdoor installations or industrial settings where the air may contain contaminants that could harm the motor.
Advantages of TEFC Motors
- Durability – The enclosed design offers superior protection against environmental factors.
- Cooling Efficiency – The external fan provides effective cooling, which is crucial for high-duty applications.
- Versatility – Suitable for indoor and outdoor applications where environmental protection is necessary.
Disadvantages of TEFC Motors
- Cost – TEFC motors are generally more expensive than ODP motors due to their complex construction and added materials for environmental protection.
- Weight – The enclosed design and additional cooling components can make TEFC motors heavier, potentially complicating installation and requiring more robust support structures.
- Cooling Efficiency – While the external fan aids in cooling, the enclosed nature of TEFC motors may limit heat dissipation compared to ODP motors, potentially making them less efficient in extremely high-temperature environments or in applications requiring continuous, high-duty operation.
Open Drip Proof (ODP) Motors
ODP motors are designed to allow air to flow freely through the motor for cooling, but also to protect against droplets of liquid falling within a 15° angle of vertical. The open slots in the motor casing permit better heat dissipation directly from the internal components to the surrounding air. However, this design is more susceptible to dust and moisture ingress than TEFC motors.
ODP motors are typically used in clean, dry indoor environments where the motor is not directly exposed to water, dust, or other contaminants. They are common in HVAC applications such as indoor air handlers, fans, and pumps operating in controlled environments.
Advantages of ODP Motors
- Cost-Effectiveness – Generally, ODP motors are less expensive than TEFC motors due to their more straightforward construction.
- Cooling Capability – The open design allows direct heat dissipation from the internal parts.
- Maintenance – Easier access for maintenance and repair due to the open construction.
Disadvantages of ODP Motors
- Environmental Vulnerability – ODP motors are more susceptible to dust, moisture, and other environmental contaminants due to their open design, which can lead to increased wear and tear.
- Limited Application – Their vulnerability to environmental factors restricts their use primarily to clean, dry indoor settings, limiting their versatility compared to TEFC motors.
- Maintenance Requirements – The exposure to environmental elements may increase the frequency of maintenance and cleaning needed to keep ODP motors operating efficiently, potentially leading to higher long-term operating costs.
TEFC vs. ODP: Making the Right Choice
When deciding between TEFC and ODP motors for HVAC systems, consider the following factors:
Environmental Conditions
TEFC motors are better for harsh, contaminated, or outdoor environments. ODP motors are suitable for clean, dry indoor settings.
Cooling Requirements
The unique cooling mechanisms of TEFC vs. ODP motors mean that the former might be better suited for high-temperature areas or situations where the motor generates considerable heat.
Cost Considerations
ODP motors may offer initial cost savings, but TEFC motors could provide better longevity and reliability in demanding conditions, potentially leading to lower long-term costs.
The choice between TEFC and ODP motor enclosures is significant for HVAC technicians and commercial HVAC purchasers. It impacts not just the upfront cost but also the operational efficiency, maintenance needs, and lifespan of HVAC equipment. By carefully considering the specific requirements of their HVAC systems and the environments in which they operate, professionals can select the motor type that best aligns with their needs, ensuring optimal performance and durability.
Remember, the right motor can significantly enhance the efficiency and reliability of HVAC systems, leading to improved comfort, reduced energy consumption, and lower operational costs over time. Therefore, dedicating effort to comprehend the differences and applications of TEFC vs. ODP motors is a prudent step for anyone involved in the selection and maintenance of HVAC systems.

