Thermostatic Expansion Valves (TXVs) are a vital component of HVAC systems. They regulate the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator coil, ensuring optimum cooling efficiency. Comprising several essential parts, such as the sensing bulb, diaphragm, and needle, TXVs precisely control refrigerant flow based on system requirements. Unlike other valves, TXVs offer superior efficiency and stability, making them an indispensable element of modern HVAC systems.

How Does a TXV Work?
A thermostatic expansion valve (TXV) is a sophisticated component that controls the amount of refrigerant flowing into the evaporator of an air conditioning or refrigeration system. This function is critical in maintaining the efficiency and performance of the system.
A sensing bulb is crucial for the TXV's operation; the bulb is filled with a fluid that expands or contracts depending on the temperature it senses. The sensing bulb is placed on the suction line, close to the evaporator outlet, where it can accurately read the temperature of the refrigerant as it leaves the evaporator. The expansion or contraction of the fluid inside the sensing bulb correlates to the superheat or the heat added to the refrigerant above its boiling point.
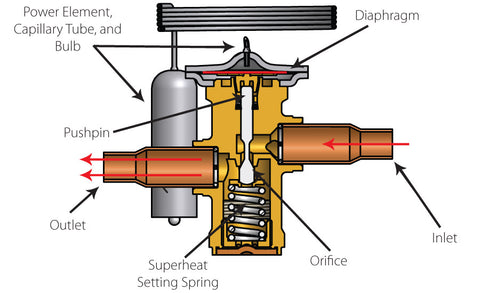
As the refrigerant temperature rises, indicating an increase in superheat, the fluid inside the sensing bulb expands. This expansion creates pressure directed to one side of a diaphragm inside the TXV. The pressure then pushes against the diaphragm, opening the valve and allowing more refrigerant to flow into the evaporator.
Conversely, when the temperature of the refrigerant drops, indicating less superheat, the fluid inside the bulb contracts and reduces the pressure on the diaphragm, allowing a spring on the opposite side of the diaphragm to push it back, reducing the valve's opening and, consequently, the refrigerant flow into the evaporator.
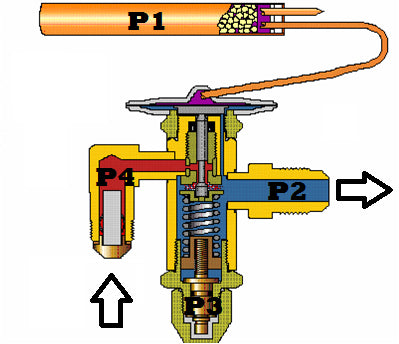
The thermostatic expansion valve continuously adjusts the flow of refrigerant into the evaporator based on the cooling load, achieving a balance that helps the system operate as efficiently as possible. This balance can also be explained with the following equation:
P1 + P4 = P2 + P3
With the following values:
- P1 = Bulb Pressure (Opening Force)
- P2 = Evaporator Pressure (Closing Force)
- P3 = Superheat Spring Pressure (Closing Force)
- P4 = Liquid Refrigerant Pressure (Opening Force)
The Impact of a TXV on System Efficiency
A TXV is essential in HVAC systems because it helps optimize performance, maintain efficiency, protect crucial components, and adapt to varying loads—contributing to the overall operational effectiveness of the system.
A TXV controls the rate at which refrigerant enters the evaporator coil. This precise control ensures the coil has the right amount of refrigerant to absorb heat effectively from the air passing over it. It thus optimizes the system's cooling performance and improves comfort levels.
The TXV also helps the system maintain efficiency by ensuring the evaporator is adequately filled with refrigerant to absorb heat but is not overly full, reducing the overall system's efficiency. Maintaining the correct superheat (the heat added to the refrigerant above its boiling point) helps maximize the refrigerant's heat-absorbing capacity, thus boosting energy efficiency.
TXVs protect the compressor, designed to compress gas, not liquid. By ensuring that all the refrigerant has been vaporized before it leaves the evaporator, the TXV prevents liquid refrigerant from entering the compressor—a phenomenon known as "liquid slugging"—which can cause severe damage to the compressor.
Additionally, TXVs respond to changes in the cooling load (the amount of heat the system needs to remove). As cooling demand increases or decreases, the TXV adjusts the flow of refrigerant to match this load. This ability makes the system more adaptable and responsive, improving comfort and efficiency.
TXV Installation & Placement
Thermostatic Expansion Valves (TXVs) should be installed between the high-pressure and low-pressure sides of a refrigeration or air conditioning system. Specifically, the TXV is typically placed at the inlet of the evaporator coil, which is on the low-pressure side of the system. The placement of the TXV at this location enables it to precisely regulate the flow of refrigerant entering the evaporator based on the cooling load.
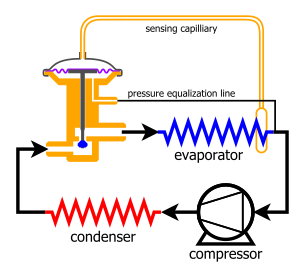
In addition to the main TXV body, there's also the sensing bulb attached to the TXV via a capillary tube. This bulb is mounted securely on the suction line (the refrigerant line leading back to the compressor from the evaporator coil). It's positioned downstream from the evaporator coil and before any heat exchangers, ideally on a straight suction line section.
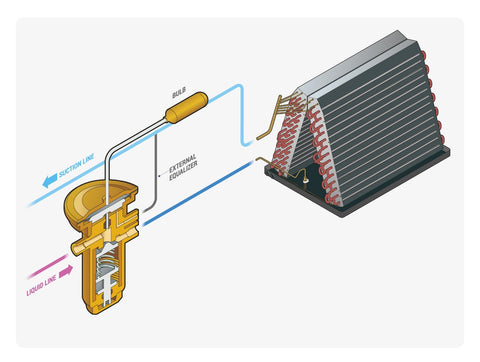
The sensing bulb's role is to monitor the temperature of the refrigerant as it leaves the evaporator, influencing the operation of the TXV. To ensure accurate temperature readings, the bulb is typically insulated to minimize the impact of ambient temperature changes.
Troubleshooting & Maintenance of TXVs
Properly maintaining and troubleshooting a Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV) ensures an HVAC system operates effectively and efficiently.
TXV Maintenance
- Inspection: Regular visual inspections should be conducted to catch any potential issues early. Look for signs of oil or refrigerant leaks around the valve, bulb, or capillary tube.
- Secure the Bulb: The bulb should be securely fastened to the suction line and insulated. If it's loose or not insulated, it may not accurately sense the suction line's temperature, leading to improper valve operation.
- Cleanliness: Keep the area around the TXV clean, and ensure there's no debris or dirt around the valve that might interfere with its operation.
- Professional Servicing: A professional HVAC technician should periodically service the system. They can check the superheat setting, ensure the TXV opens and closes properly, and that the refrigerant level and pressure are correct.
TXV Troubleshooting
If you suspect a problem with the TXV, here are some steps for troubleshooting:
- Superheat Measurement: Check the superheat setting of the TXV by measuring the temperature and pressure at the outlet of the evaporator and using these values to calculate the superheat. If the superheat value is too high or too low, the TXV might not function properly.
- Check for Blockage or Stuck Valve: If the superheat is too high, the TXV may be stuck closed, or there could be a blockage. If it's too low, the TXV might be stuck open.
- Sensing Bulb Position: Ensure the sensing bulb is correctly positioned, securely attached to the suction line, and well insulated.
- Temperature and Pressure: Check the refrigerant pressure and temperature before and after the TXV. An unusually large drop may indicate a problem with the TXV.
- Check for Refrigerant Charge: An undercharged or overcharged system can cause the TXV to behave erratically.
- Professional Diagnosis: If the problem persists after the preliminary checks, it's advisable to have a trained HVAC technician diagnose the issue. They can use specialized equipment to check the TXV's operation more accurately and determine whether it needs to be repaired or replaced.
TXVs by Manufacturer
Carrier TXVs
Carrier expansion valves are critical components used in refrigeration and air conditioning systems to regulate the flow of refrigerant, allowing it to expand or contract as needed.
Shop Carrier Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Trane Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Serving a crucial role in Trane HVAC systems, these valves control the flow of refrigerant, adapting to fluctuating demand to maintain an optimal balance between system performance and efficiency. They play a significant role in avoiding system overheating and pressure imbalances.
Shop Trane Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Daikin Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Daikin TXVs regulate the flow of refrigerant in HVAC systems, adjusting to changes in demand and maintaining an optimal balance between efficiency and performance. These valves are critically important to the system's operation, as they help avoid overheating and pressure imbalances.
Shop Daikin Thermostatic Expansion Valves
York Thermostatic Expansion Valves
York TXVs control the flow of refrigerant, adapting to changing demands to balance system efficiency and performance. Their role is critical in preventing system overheating and maintaining pressure stability.
Shop York Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Lennox Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Lennox TXVs administer the flow of refrigerant, adjusting to demand variations to uphold a harmonious balance between system efficiency and output. Their function helps prevent overheating and maintain pressure equilibrium.
Shop Lennox Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Johnson Controls Thermostatic Expansion Valves
Johnson Controls TXVs manage the refrigerant flow, adapting to fluctuating demand to maintain balance between system performance and efficiency. Their role is fundamental in avoiding issues like system overheating and pressure discrepancies.
Shop Johnson Controls Thermostatic Expansion Valves
AAON Thermostatic Expansion Valves
AAON thermostatic expansion valves are critical components in refrigeration and air conditioning systems. These valves regulate the flow of refrigerant, allowing it to expand or contract, which is essential for achieving the desired cooling or heating effect in the system.

